
Table of Content
Discovering the Difference Between JPEG and PNG, and When to Use Each
Every one of us, at one time or another, have faced the dilemma – to save our images, but with no idea whether to do so in the PNG or JPEG format. This JPEG vs PNG debate is a long-running tale of pros and cons, with neither side willing to give in to the superiority of their preferred image format.
Since the advent of digital imagery and graphic design, people have been trying to come up with various image formats that could be used to save them at the smallest size possible, without losing the details. And although both PNG and JPEG are raster-based image formats, which is something to remember about them both, each of them have their own advantages depending on the application. That is why any professional graphics agency you go to will have them using these files to clients along with vector-based files like SVG or AI files.
But why? Why are these image formats still used? What was their original purpose, and when should you use each of these image formats?
Let’s join us and discover the art of, and what each of them can be used for.
JPEG Vs. PNG – An Overview of the Image Format Debate
When we talk about JPEG vs PNG, there is often no clear difference between the two, as might be between a vector or raster image. And as we mentioned at the start, both PNG and JPEG are raster-type image formats. That means that these image formats manipulate graphics at the pixel level, unlike vector-type formats.
Now, raster-type files have many cons, such as loss of details when compressing images, as well as image deterioration when increasing or decreasing its dimensions. And that bring us to the difference between JPEG and PNG.
PNG is considered a Lossless image format, meaning that the quality of the graphics remains more or less the same before and after compression. Notice that I use the word considered here, because PNG as a raster type is inherently lossy compared to vector graphics formats.
JPEG, or JPG, on the other hand, is considered a somewhat Lossy format compared to PNG. That is why it is used to compress and store images for everyday use.
Now, by the descriptions above, you might have understood that the most basic difference between the two has to do with the quality of the final image. One gives virtually the same image as the original, while the other loses some of its detail. So you might be wondering, that in today’s day and age, when huge amounts of storage is available for a fraction it was a few years ago, why would someone use a lossy format over a virtually lossless format?
Well, this decision between PNG vs JPEG file format boils down to one simple thing – application. Now, while its great to have higher quality images that have little to no loss in quality, lower quality images can sometimes be a godsend, especially when different types of graphic design demand it.
JPG Vs. JPEG – What Do You Call It, and What to Use it For?
JPEG, also known as JPG, stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group. It is the standard image format used to store compressed image data when a smaller size is desired, at the expense of a little loss of quality.
Now, when we talk about a little loss of quality, rest assured that it is very little. Often, you would have a hard time even identifying whether the image lost some level of detail. This means that while the compression format drops the file size drastically, the result is still of reasonably acceptable quality.
PNG – What Does Portable Network Graphics Represent for Image Formats?
PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics, and is a lossless graphics compression format. It was originally conceived as an improved replacement to the GIF file format. Its purpose was to transfer images to the internet in reasonable quality, but not for print. That is why it only supports RGB/RGBA color palettes instead of CMYK.
And despite being virtually lossless, the file sizes are relatively small, making it perfect for digital uses such as websites, social media, and more.
Applications for Using JPEG and PNG – What Sets Each Image Format Apart?

As we discussed earlier, we cannot judge the suitability of an image format based purely on the quality of image it produces. Each compression format has its own place, such as JPG being the popular choice for storing large quantities of images within a limited storage limit. Therefore, as PNG and JPG has entirely different purposes, the Jpeg vs PNG debate is a moot point.
PNG was specifically created as a mode of transferring images over the internet, something previously done using the GIF format. Images compressed using the PNG format can be palette-based color combinations, RGB/RGBA full color, or even grayscale, but doesn’t support print color schemes like pantone or CMYK.
The best feature of PNG, which JPG lacks, is its ability to store and address transparencies. That means that this compression format is best where the image background needs to be transparent, such as for logo files. Moreover, it is also the format of choice where the image needs to portray fade effects.
The Jpeg compression format, on the other hand, has been primarily used for processing and producing digital photographs and graphics where complex shading and palette is needed without a huge file size.
Compared to PNG, JPG’s 10-to-1 compression ratio makes quality loss unavoidable. However, despite the smaller size, the images are still vibrant. That makes it a great format to store and share photographs over the internet.
While it may offer great results in photographs and other rich graphics, it works dismally for line drawings, textual imagery, and other graphics like them. That is because the sharp contrast required for such imagery requires lossless compression, which is something JPG doesn’t provide.
Is PNG Better Than JPEG for Printing?
While neither is specifically designed for printing, if you need to use either of these formats, the choice of compression format depends on what you want to print. For photos, JPEG would be the format of choice for photos, as it is the compression style used commonly for digital photographs and graphics with vibrant and life-like color schemes.
However, if you need to print some kind of illustration or design with fine lines or stark contrast, PNG is the format of choice. This goes for designs such as logo files with intricate logo fonts, or other graphics where sharpness of the design is necessary for the overall effect.
Difference Between PNG and JPG for the Web?
When it comes to judging JPEG vs PNG purely on the basis of quality, PNG recreates more vibrant and true-to-original compressed images. That is because unlike JPG, PNG actually stores transparencies, which makes the end result virtually lossless. This means that when it comes to the difference between JPEG and PNG, it is about the way each format saves images.
PNG Vs. JPEG – Differences in Size Between Files of Each Format
The size difference for JPEG vs PNG varies greatly, depending on the image being compressed. If the image has a lot of fade effects and transparencies, then the PNG will be quite larger than the JPG file. However, for simpler images, the difference in file size will not be that huge, as the core purpose of both image formats is to provide the best image quality for storage and sharing, with the best quality possible.
Choosing Between JPEG Vs. PNG for the Preferred Image Format in Your Project
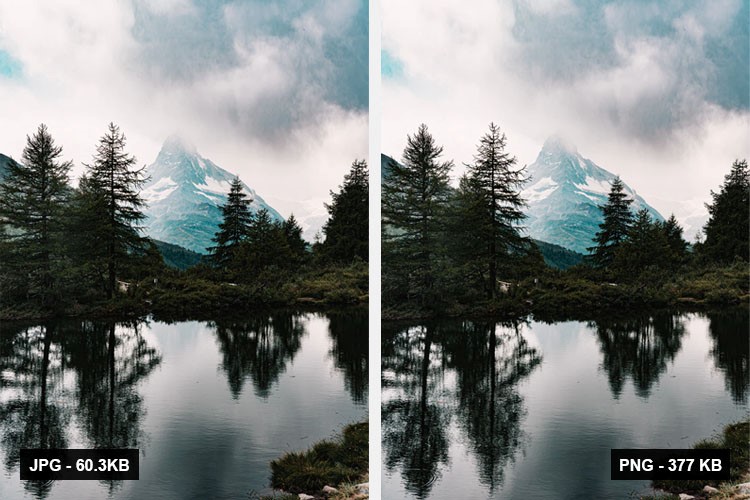

As we discussed before, the choice of opting for JPG vs PNG compression format depends entirely upon what you want to do with the image you receive at the end. If you want to store a large number of images in a limited storage space, with sufficient quality to enable sharing via the web, go for JPEG.
However, if you want to portray the image online with all of its fade effects and transparencies, then PNG is the format for you.
Asking Yourself – Is PNG or JPEG Better for My Project?
Suppose you have edited a set of images from your last family dinner, and want to save them to the cloud as part of your family keepsakes. However, storing them in RAW or other formats would take up too much space, which is usually limited for many of us.
Now comes the part where many who are unaware of the Jpeg vs PNG qualities would end up making the wrong choice. But now that you know the purpose for each of these compression formats, you will be able to make the right choice and save your valuable memories in the right image format.
Difference Between JPEG and PNG – A Summary
Essentially, there are four factors around which the entire debate about the JPEG vs. PNG boils down to. These factors include:
- Lossy vs Lossless Compression
- Image File Size
- Addressing Transparency and Layers
- Digital Images and Graphics
Let’s talk about them in a little detail.
Lossy vs Lossless Compression
As we discussed earlier, PNG format is considered a lossless image format for a vector graphics format, which means that it would generally retain more detail than JPEG, which is a lossy format. And while both have their own applications, in this JPEG vs PNG debate, this is a factor won by PNG.
Image File Size
Storing a greater amount of detail comes with its own problems, such as having a larger file size than its more compressed counterparts. PNG, in order to retain as much detail as possible to be considered a lossless format, loses this factor to JPEG, where the biggest difference between JPEG and PNG is their file size.
Addressing Transparency and Layers
The reason PNG has such great detail compared to other vector graphics formats like JPEG, is because it saves transparencies and layers in an image for better quality post-compression. JPEG on the other hand, does not do so, and thus it doesn’t cater to transparency in an image. In fact, that is exactly what makes JPEG the preferred choice for print over PNG images.
Digital Images and Graphics
If you are going to save images such as photographs, then JPEG is the format to go. However, if you want to retain the fine details such as line clarity, colors, background transparencies, and more, than PNG should be your preferred choice in the JPEG vs PNG debate.
Frequently Asked Questions
| Is EXIF data from digital photographs supported by either JPEG or PNG? Yes. Jpeg format does use the EXIF to display data like shutter speed, focal length, etcetera. |
| Are JPEGs and PNGs raster files? Yes, they are both types of raster image formats. |
| Do JPEG or PNG support CMYK? While JPEG can support CMYK, many programs find it difficult to render them in this format, and thus are quite rare. |
| Do size limits apply to JPEG and PNG files? While PNG has an unlimited size allowance theoretically, it is bound by factors such as memory constraints. JPEG has a size limit of 65, 535 pixels for its height. |
| Why do people often use JPEG in JPG vs PNG for photographs? It is because JPEGs retain a decent amount of information in a relatively small file size, perfect for applications such as photographs and more. |
| What is the best quality image format, even better than the JPEG vs PNG options? TIFF is considered the best image format, used for high-resolution printing, art photography, and other artistic applications. That is because it retains a high level of quality due to its lossless compression format, perfect for scanned and printed documents. |
Conclusion
When learning how to design a logo or any graphic design, knowing which image compression format works for what purpose is an integral part of that process. The Jpeg vs PNG debate is one where many new designers get confused. But now that you know the difference between the two, you will be able to go on your way, using the best compression method every time.

Logopoppin
Logopoppin is a graphic design agency that specializes in logo designing, web development, video production and advanced branding services. We love to innovate businesses with new age technologies, allowing them to improve their visual reputation.



